Archaeologists in Luxembourg have discovered a lavish 1,700-year-old hoard of Roman gold coins that had been placed near the foundations of a small, tower-like Roman fort.
The team unearthed 141 gold coins, which were minted between A.D. 364 and 408, in Holzthum, a village in northern Luxembourg. The coins feature portraits of eight emperors, but three coins portrayed an unexpected ruler: Eugenius, an illegitimate emperor of the Western Roman Empire who reigned for only two years (392 to 394).
This usurper, Eugenius, a rhetoric teacher and court official, was proclaimed emperor of the West by a powerful military officer, months after the western emperor Valentinian II was found hanged under mysterious circumstances. However, Theodosius I, the Christian emperor in the East, refused to recognize Eugenius and disapproved of his supposed policy of religious tolerance. This led to armed conflict and culminated in Eugenius’ bloody defeat and death at the Battle of Frigidus in September 394. His coins are especially rare because his time in power was so short.
“This is a major archaeological discovery, as it is extremely rare to be able to study an entire ancient monetary deposit in its archaeological context,” researchers wrote in a translated statement from the National Institute for Archaeological Research (INRA) in Luxembourg.
Because of its historical significance, the find was kept secret for almost four years, with excavations under the direction of INRA taking place from 2020 to 2024. The team also faced hazardous conditions, as there were multiple World War II munitions and explosives buried in the area, prompting the Luxembourg Army Mine Action Service (SEDAL) to help with the dig.
Related: Amateur freedivers find gold treasure dating to the fall of the Roman Empire
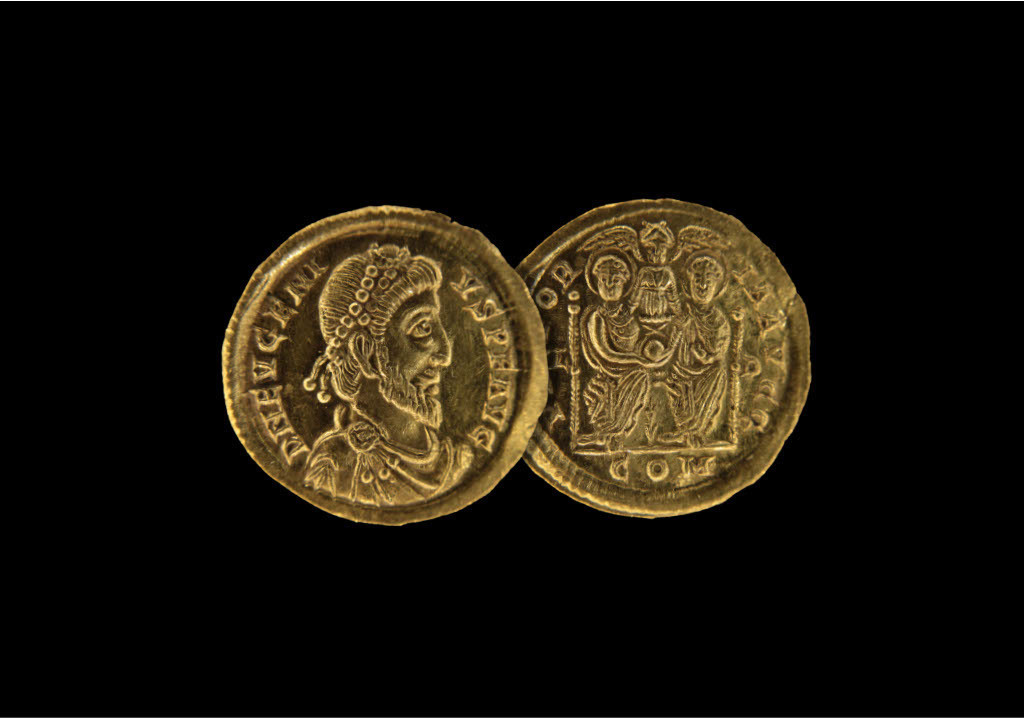

Worth nearly $322,000
The gold coins are solidi, a term that comes from the Latin “solidus,” meaning “solid” — a reference to their consistently reliable gold content. The coins, each of which weighs approximately 0.16 ounce (4.5 grams), were introduced at the beginning of the fourth century during the era of the “Later Roman Empire.” The solidus remained relatively stable for centuries and spread throughout the entire Mediterranean region.

Following an independent analysis, which considered the “excellent condition” of the coins and “the presence of some rare specimens,” the coins were valued at 308,600 euros, or nearly $322,000. In accordance with the legal provisions on cultural heritage, this sum is reserved for those who have legal rights, such as property holders, over the find.
“It will still take some time to process the excavations and finds,” Luxembourg Culture Minister Eric Thill said in a translated parliamentary statement, “but it will undoubtedly increase our knowledge and understanding of the last century of the Roman Empire in the West.”
The researchers plan to analyze the hoard further and eventually publish the results in a research journal.







Leave a Comment