The last two years exceeded on average a critical warming limit for the first time as global temperatures soar “beyond what modern humans have ever experienced”, Europe’s climate monitor said Friday.
This does not mean the internationally-agreed 1.5C warming threshold has been permanently breached, but the Copernicus Climate Change Service said it was drawing dangerously near.
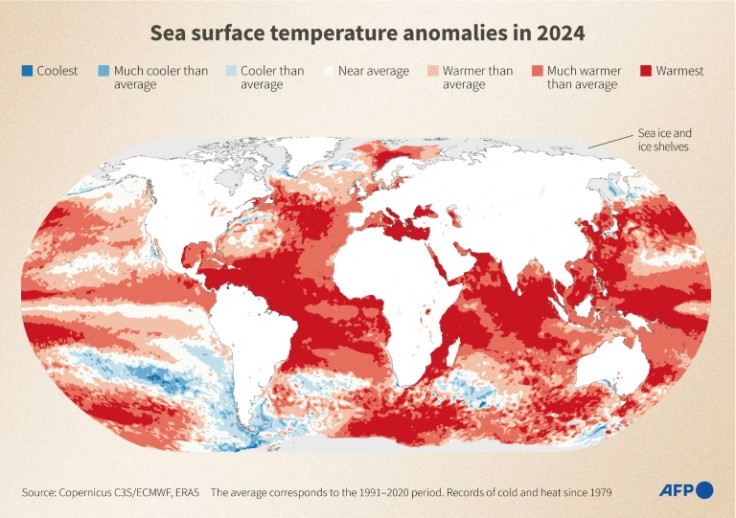
Copernicus confirmed that 2024 was the hottest year on record, surpassing 2023 and extending a streak of extraordinary heat that fuelled climate extremes on all continents.
Another record-breaking year is not anticipated in 2025, as climate sceptic Donald Trump takes office, and a deadline looms for nations to commit to curbing rising levels of greenhouse gases.
But scientists predict that 2025 will likely still rank among the top three warmest years in the history books.
This excess heat supercharges extreme weather, and 2024 saw countries from Spain to Kenya, the United States and Nepal hit by disasters that cost more than $300 billion by some estimates.
Los Angeles is battling deadly wildfires that have destroyed thousands of buildings and forced tens of thousands to flee their homes. US President Joe Biden said the fires were the most “devastating” to hit California and were proof that “climate change is real”.
Copernicus said sustained, unprecedented warming made average temperatures over 2023 and 2024 more than 1.5 degrees Celsius hotter than pre-industrial times.
This “should alarm us all”, Britain’s Energy Security Minister Ed Miliband said on Friday.
“The climate crisis is here and now and getting worse. Sticking our head in the sand would be a betrayal of future generations.”
Nearly 200 nations agreed in Paris in 2015 that meeting 1.5C offered the best chance of preventing the most catastrophic repercussions of climate change.
But the world is nowhere on track to meeting that target.
“We are now teetering on the edge of passing the 1.5C level,” said Copernicus climate deputy director Samantha Burgess.
Copernicus records go back to 1940 but other sources of climate data, such as ice cores and tree rings, allow scientists to say the Earth today is likely the warmest its been in tens of thousands of years.
The 1.5C threshold is measured in decades, not individual years, but Copernicus said reaching this limit even briefly illustrated the unprecedented changes being brought about by humanity.
Scientists say every fraction of a degree above 1.5C is consequential, and that beyond a certain point the climate could shift in ways that are difficult to anticipate.
At present levels, human-driven climate change is already making droughts, storms, floods and heatwaves more frequent and intense.
The death of 1,300 pilgrims in Saudi Arabia from extreme heat, a barrage of powerful tropical storms in Asia and North America, and historic flooding in Europe and Africa marked grim milestones in 2024.
The oceans, a crucial climate regulator which absorb 90 percent of excess heat from greenhouse gases, warmed to record levels in 2024, straining coral reefs and marine life and stirring violent weather.
Warmer seas mean higher evaporation and greater moisture in the atmosphere, causing heavier rainfall, feeding energy into cyclones and bringing sometimes unbearable humidity.
Water vapour in the atmosphere hit fresh highs in 2024 and combined with elevated temperatures caused floods, heatwaves and “misery for millions of people”, Burgess said.
Johan Rockstrom of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research said hitting 1.5C was a “stark warning sign”.
“We have now experienced the first taste of a 1.5C world, which has cost people and the global economy unprecedented suffering and economic costs,” he told AFP.
Scientists say the onset of a warming El Nino phenomenon in 2023 contributed to the record heat that followed.
But El Nino ended in early 2024, and scientists have puzzled over why global temperatures have remained at record or near-record levels ever since.
In December, the World Meteorological Organization said if an opposite La Nina event took over in coming months it would be too “weak and short-lived” to have much of a cooling effect.
“The future is in our hands — swift and decisive action can still alter the trajectory of our future climate,” said Copernicus climate director Carlo Buontempo.
Nations agreed to transition away from fossil fuels at a UN summit in 2023 but the latest meeting in November struggled to make any progress around how to make deeper reductions to heat-trapping emissions.
AFP







Leave a Comment