A Chinese research team is developing a lightweight robotic drone with a targeted special mission scenario of Mars exploration.
The air-ground dual-purpose unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) weighs only 10.6 ounces (300 grams), equivalent to the weight of an apple. The development team is at the School of Astronautics (SoA) of the Harbin Institute of Technology.
Seen as showing promising potential in future Mars science work, the UAV can take off at any time, traverse obstacles, and boasts superb endurance, reports state-owned China Central Television (CCTV).
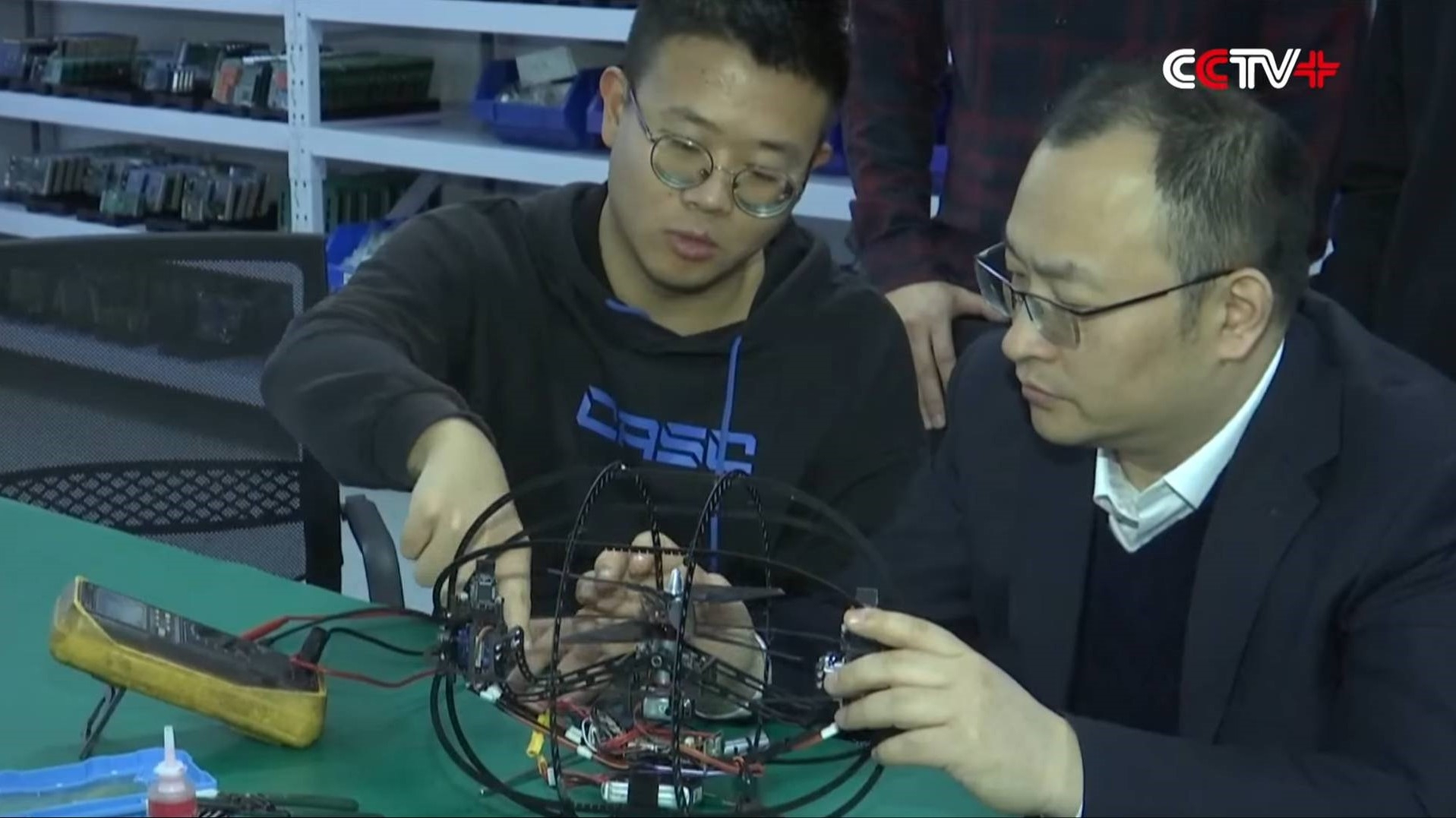
“On the ground, it mainly rolls by shifting its center of gravity,” said Zhu Yimin, a Ph.D candidate at SoA.
“In the air, it relies on a pair of contra-rotating coaxial rotors, controlled by a steering engine to adjust the forward direction, to control torque and force, ultimately achieving stable flight,” Zhu told CCTV.
Related: Will China return Mars samples to Earth before the US does?
Multiple models
The UAV work entails multiple models of air-ground dual-mode robots with different configurations, CCTV reports. These robots move by rolling close to the ground, which reduces energy consumption, and can achieve a flight endurance time of more than six times that of traditional drones of the same size.
According to Zhang Lixian, a professor within the SoA, the hope is that the aerial vehicle can show off its long endurance and observational abilities on Mars.
“Our second goal is for such machines to be suitable for construction in many underground spaces and for exploring unknown underground spaces. We also need robotic means for inspection and environmental detection. We have now materialized all these functions,” said Zhang.
NASA’s Ingenuity
The Chinese aerial drone work is taking a different approach than NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter. That history-making autonomous aircraft operated for nearly three years of flight on Mars, making 72 flights within Jezero Crater.
Dispatched by NASA’s Perseverance rover, Ingenuity weighed 4 pounds on Earth (1.81 kilograms), which is equivalent to 1.5 pounds (0.68 kg) on Mars.
Ingenuity first lifted off the Martian surface on April 19, 2021 and made its last flight on Jan. 18, 2024. On Flight 72, rotor blades on the craft were damaged during landing, permanently grounding the vehicle.
As the first aircraft on another world, Ingenuity flew more than 14 times farther than planned while logging more than two hours of total flight time.
For a video look at the potential Mars craft being developed by China, go here.






Leave a Comment