The most important Earth news in 2024 was undoubtedly the most depressing: Climate change wreaked havoc around the globe, indirectly causing flooding, drought, wildfires and other extreme weather events.
This year is on track to become the warmest year since records began and the first year that global temperatures have been 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above preindustrial levels.
In May, levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere — as measured from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Mauna Loa Observatory — reached a record high of 426.90 parts per million. “Not only is CO2 now at the highest level in millions of years, it is also rising faster than ever,” Ralph Keeling, director of the Scripps CO2 Program, said in a statement at the time. Global carbon emissions from fossil fuels also reached a new record high.
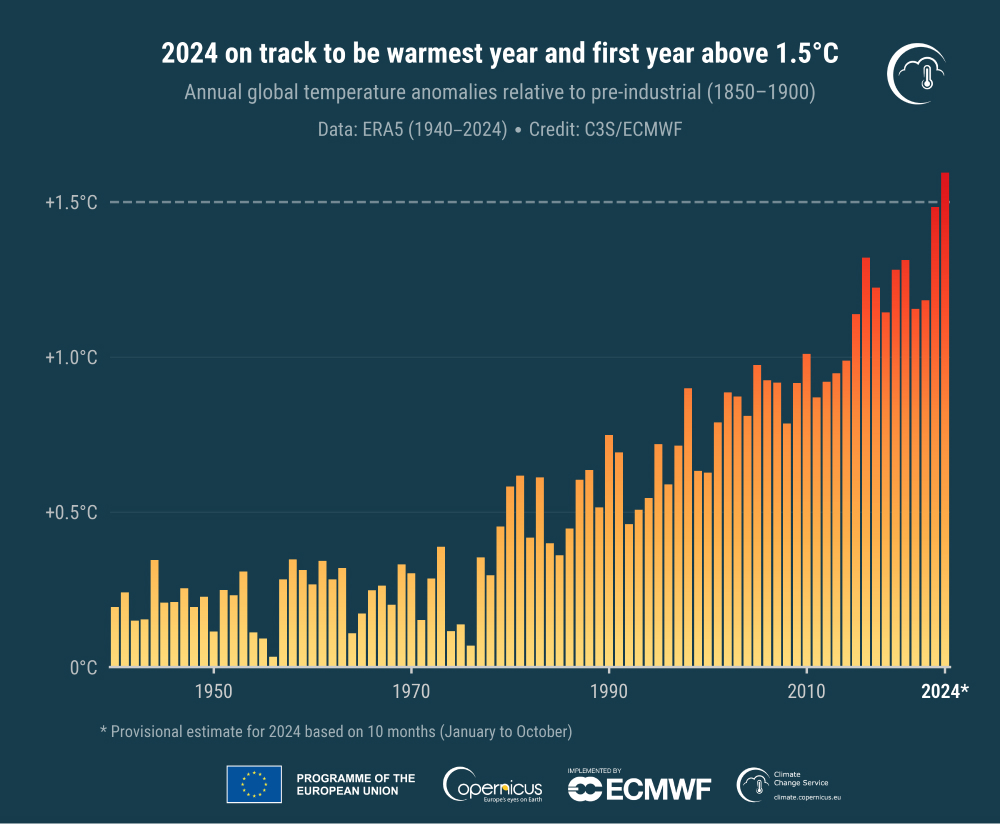
All that warming has had disastrous impacts on weather around the globe. The year started with one of the strongest El Niño events on record. That led to a devastating hurricane season that culminated in the deadliest storm to hit the continental U.S. in decades. El Niño also fueled a severe drought in the Amazon. This prolonged drought made the rainforest “more flammable” — an impact that led to the worst wildfire season in nearly 20 years.

And in Spain, torrential rain led to flash floods that killed over 200 people. Scientists also linked this dramatic weather event to climate change.
Climate change devastation edging closer
But some of the scariest news about the planet isn’t what happened this year but rather what could occur if we don’t stop spewing carbon into the atmosphere. A study published in June suggested ecological tipping points — such as the collapse of the Greenland Ice Sheet and the transformation of the Amazon rainforest into savanna — could be reached in just 15 years if climate change isn’t controlled.
In October, scientists penned an open letter warning about the risk posed by the collapse of a key Atlantic current. In it, researchers urged policymakers to address the threat posed by the weakening Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) — a giant ocean conveyor belt that transports heat to the Northern Hemisphere, and the breakdown of which could cause temperatures across Europe to plummet.
We’ve also been warned that we’re facing a global water crisis due in part to climate change and chronic mismanagement of resources. “For the first time in human history, we are pushing the global water cycle out of balance,” Johan Rockström, director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and co-chair of the Global Commission on the Economics of Water, which produced the report, said in a statement. “Precipitation, the source of all freshwater, can no longer be relied upon due to human caused climate and land use change, undermining the basis for human wellbeing and the global economy.”
Still, it’s not too late to avert some of the worst of these futures. Michael Mann, presidential distinguished professor and director of the Center for Science, Sustainability and the Media at the University of Pennsylvania, believes it’s not too late to stop the worst effects of climate change. “We [climate scientists] have, in some ways, failed to communicate that we can still avert catastrophic climate change,” he wrote for Live Science in November.
“We actually decide how bad the climate crisis will get. There is still time to preserve our ‘fragile moment,’ but the window of opportunity is narrowing. There is urgency in reducing carbon emissions. But there is also still agency on our part in acting.”







Leave a Comment